During the rebuild of the wheelchair motors for the support trolley, I found myself needing an accurate milliohm meter to test the armature windings with. Commercial instruments like these are expensive, but some Google searching found a milliohm meter project based around the Arduino from Circuit Cellar.
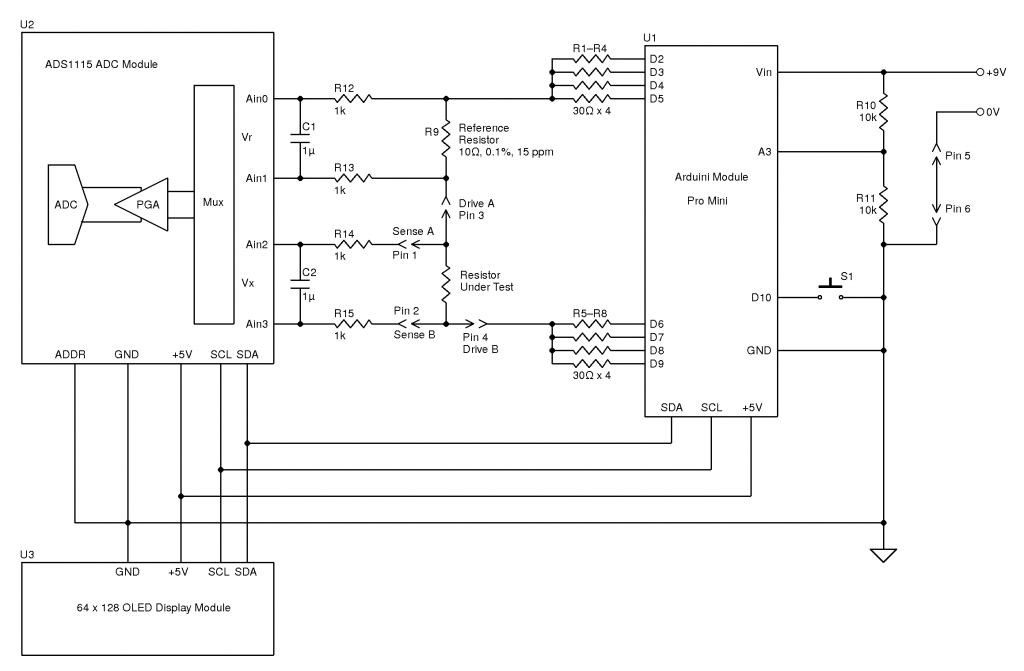
Here’s the original author’s circuit diagram, paralleling nearly all of the Arduino’s digital output pins together to source/sink the test current, an ADS1115 ADC to take more accurate readings, with the results displayed on a jellybean 128×64 OLED module. The most expensive part here is the 10Ω 0.1% 15ppm reference resistor, R9.
I decided to make some small adjustments to the power supply section of the project, to include a rechargeable lithium cell rather than a 9v PP3 battery. This required some small changes to the Arduino sketch, a DC-DC boost converter to supply 5v from the 3.7v of a lithium cell, a charger module for said cell, and with the battery voltage being within the input range of the analogue inputs, the voltage divider on A3 was removed. A new display icon was also added in to indicate when the battery is being charged, this uses another digital input pin for input voltage sensing.
I also made some basic changes to the way an unreadable resistance is displayed, showing “OL” instead of “—–“, and the meter sends the reading out over the I²C bus, for future expansion purposes. The address the data is directed to is set to 0x50.
I’ve not etched a PCB for this as I couldn’t be bothered with the messy etchant, so I built this on a matrix board instead.
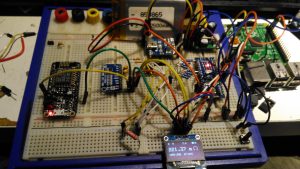
Since I made some changes to both the software and the hardware components, I decided to prototype the changes on breadboard. The lithium cell is at the top of the image. with the charger module & DC-DC converter. The Arduino Nano is on the right, the ADC & reference resistor on the left, and the display at the bottom.
The Raspberry Pi & ESP8266 module are being used in this case to discharge the battery quicker to make sure the battery level calibration was correct, and to make sure the DC-DC converter would continue to function throughout the battery voltage range.

Here’s the final board with the passive components installed, along with the DC-DC converter. I used a Texas Instruments PTN04050 boost module for power as I had one spare.

The bottom of the board has most of the wire jumpers for the I²C bus, and power sensing.

Here’s both modules installed on the board. I used an Arduino Nano instead of the Arduino Pro Mini that the original used as these were the parts I had in stock. Routing the analogue pins is also easier on the Mini, as they’re brought out to pins in the DIP footprint, instead of requiring wire links to odd spots on the module. To secure the PCB into the case without having to drill any holes, I tapped the corner holes of the matrix board M2.5 & threaded cap head screws in. These are then spot glued to the bottom of the case to secure the finished board.

The lithium charger module is attached to the side of the enclosure, the third white wire is for input sensing – when the USB cable is plugged in a charge icon is shown on the OLED display.

The inputs on the side of the enclosure. I’ve used the same 6-pin round connector for the probes, power is applied to the Arduino when the probes are plugged in.

Everything installed in the enclosure – it’s a pretty tight fit especially with the lithium cell in place.

The top cover has the Measure button, and the OLED display panel, the latter secured to the case with M2.5 cap head screws.

Finally, the measurement loom, with Kelvin clips. These were an eBay buy, keeping things cheap. These clips seem to be fairly well built, even if the hinges are plastic. I doubt they’re actually gold-plated, more likely to be brass. I haven’t noticed any error introduced by these cheap clips so far.
The modified sketch is below:
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Simple, accurate milliohmeter
//
// (c) Mark Driedger 2015
//
// - Determines resistance using 4 wire measurement of voltage across a series connected
// reference resistor (Rr, 10 ohm, 0.1%) and test resistor (Rx)
// - range of accurate measurement is roughly 50 mohm to 10Kohm
// - Uses Arduino digital I/O ports to deliver the test current, alternating polarity to cancel
// offset errors (synchronous detector)
// - 4 I/O pins are used for each leg of the test current to increase test current
// - Averages 2 cycles and 100 samples/cycle
// - Uses a 16 bit ADC ADS1115 with 16x PGA to improve accuracy
//
// Version History
// May 24/15 v1.0-v4.0
// - initial development versions
// May 27/15 v5.0
// - changed display to I2C
// - backed out low power module since it seemed to cause serial port upload problems
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
#include <Wire.h>
#include <SPI.h>
#include <Adafruit_GFX.h>
#include <Adafruit_SSD1306.h>
//#include <LowPower.h>
#if (SSD1306_LCDHEIGHT != 64)
#error("Height incorrect, please fix Adafruit_SSD1306.h!");
#endif
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// I/O port usage
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// serial port (debug and s/w download) 0, 1
// I²C interface to ADC & display A4, A5
// positive drive 2, 3, 4, 5
// push to test input 8
// unused 9, 10, 11, A0, A1, A2, A6, A7
// negative drive 6, 7, 8, 9
// battery voltage monitor A3
// debug output 13
#define P_PushToTest 10 // push button (measure), active low
#define P_Debug 13
#define CHG 12
// ADS1115 mux and gain settings
#define ADS1115_CH01 0x00 // p = AIN0, n = AIN1
#define ADS1115_CH03 0x01 // ... etc
#define ADS1115_CH13 0x02
#define ADS1115_CH23 0x03
#define ADS1115_CH0G 0x04 // p = AIN0, n = GND
#define ADS1115_CH1G 0x05 // ... etc
#define ADS1115_CH2G 0x06
#define ADS1115_CH3G 0x07
#define ADS1115_6p144 0x00 // +/- 6.144 V full scale
#define ADS1115_4p096 0x01 // +/- 4.096 V full scale
#define ADS1115_2p048 0x02 // +/- 2.048 V full scale
#define ADS1115_1p024 0x03 // +/- 1.024 V full scale
#define ADS1115_0p512 0x04 // +/- 0.512 V full scale
#define ADS1115_0p256 0x05 // +/- 0.256 V full scale
#define ADS1115_0p256B 0x06 // same as ADS1115_0p256
#define ADS1115_0p256C 0x07 // same as ADS1115_0p256
Adafruit_SSD1306 display(0); // using I2C interface, no reset pin
static int debug_mode = 0; // true in debug mode
float ADS1115read(byte channel, byte gain)
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// reads a single sample from the ADS1115 ADC at a given mux (channel) and gain setting
// - channel is 3 bit channel number/mux setting (one of ADS1115_CHxx)
// - gain is 3 bit PGA gain setting (one of ADS1115_xpxxx)
// - returns voltage in volts
// - uses single shot mode, polling for conversion complete, default I2C address
// - conversion takes approximatly 9.25 msec
//--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
{
const int address = 0x48; // ADS1115 I2C address, A0=0, A1=0
byte hiByte, loByte;
int r;
float x;
channel &= 0x07; // constrain to 3 bits
gain &= 0x07;
hiByte = B10000001 | (channel<<4) | (gain<<1); // conversion start command
loByte = B10000011;
Wire.beginTransmission(address); // send conversion start command
Wire.write(0x01); // address the config register
Wire.write(hiByte); // ...and send config register value
Wire.write(loByte);
Wire.endTransmission();
do // loop until conversion complete
{
Wire.requestFrom(address, 2); // config register is still addressed
while(Wire.available())
{
hiByte = Wire.read(); // ... and read config register
loByte = Wire.read();
}
}
while ((hiByte & 0x80)==0); // upper bit (OS) is conversion complete
Wire.beginTransmission(address);
Wire.write(0x00); // address the conversion register
Wire.endTransmission();
Wire.requestFrom(address, 2); // ... and get 2 byte result
while(Wire.available())
{
hiByte = Wire.read();
loByte = Wire.read();
}
r = loByte | hiByte<<8; // convert to 16 bit int
switch(gain) // ... and now convert to volts
{
case ADS1115_6p144: x = r * 6.144 / 32768.0; break;
case ADS1115_4p096: x = r * 4.096 / 32768.0; break;
case ADS1115_2p048: x = r * 2.048 / 32768.0; break;
case ADS1115_1p024: x = r * 1.024 / 32768.0; break;
case ADS1115_0p512: x = r * 0.512 / 32768.0; break;
case ADS1115_0p256:
case ADS1115_0p256B:
case ADS1115_0p256C: x = r * 0.256 / 32768.0; break;
}
return x;
}
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Drive functions
// - ports 4-7 and A0-A3 are used to differentially drive resistor under test
// - the ports are resistively summed to increase current capability
// - DriveOff() disables the drive, setting the bits to input
// - DriveOn() enables the drive, setting the bits to output
// - DriveP() enables drive with positive current flow (from ports 4-7 to ports A0-A3)
// - DriveN() enables drive with negative current flow
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void DriveP()
{
DriveOff();
digitalWrite( 2, HIGH);
digitalWrite( 3, HIGH);
digitalWrite( 4, HIGH);
digitalWrite( 5, HIGH);
digitalWrite( 6, LOW);
digitalWrite( 7, LOW);
digitalWrite( 8, LOW);
digitalWrite( 9, LOW);
DriveOn();
}
void DriveN()
{
DriveOff();
digitalWrite( 2, LOW);
digitalWrite( 3, LOW);
digitalWrite( 4, LOW);
digitalWrite( 5, LOW);
digitalWrite( 6, HIGH);
digitalWrite( 7, HIGH);
digitalWrite( 8, HIGH);
digitalWrite( 9, HIGH);
DriveOn();
}
void DriveOn()
{
pinMode( 2, OUTPUT); // enable source/sink in pairs
pinMode( 6, OUTPUT);
pinMode( 3, OUTPUT);
pinMode( 7, OUTPUT);
pinMode( 4, OUTPUT);
pinMode( 8, OUTPUT);
pinMode( 5, OUTPUT);
pinMode( 9, OUTPUT);
delayMicroseconds(5000); // 5ms delay
}
void DriveOff()
{
pinMode( 2, INPUT); // disable source/sink in pairs
pinMode( 6, INPUT);
pinMode( 3, INPUT);
pinMode( 7, INPUT);
pinMode( 4, INPUT);
pinMode( 8, INPUT);
pinMode( 5, INPUT);
pinMode( 9, INPUT);
}
int CalcPGA(float x)
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Calculate optimum PGA setting based on a sample voltage, x, read at lowest PGA gain
// - returns the highest PGA gain that allows x to be read with 10% headroom
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
{
x = abs(x);
if (x>3.680) return ADS1115_6p144;
if (x>1.840) return ADS1115_4p096;
if (x>0.920) return ADS1115_2p048;
if (x>0.460) return ADS1115_1p024;
if (x>0.230) return ADS1115_0p512;
else return ADS1115_0p256;
}
void BatteryIcon(float charge)
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Draw a battery charge icon into the display buffer without refreshing the display
// - charge ranges from 0.0 (empty) to 1.0 (full)
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
{
static const unsigned char PROGMEM chg[] = // Battery Charge Icon
{ 0x1c, 0x18, 0x38, 0x3c, 0x18, 0x10, 0x20, 0x00 };
int w = constrain(charge, 0.0, 1.0)*16; // 0 to 16 pixels wide depending on charge
display.drawRect(100, 0, 16, 7, WHITE); // outline
display.drawRect(116, 2, 3, 3, WHITE); // nib
display.fillRect(100, 0, w, 7, WHITE); // charge indication
//battery charging indication
pinMode(CHG, INPUT);
if (digitalRead(CHG) == HIGH)
display.drawBitmap(91, 0, chg, 8, 8, WHITE);
}
void f2str(float x, int N, char *c)
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Converts a floating point number x to a string c with N digits of precision
// - *c must be a string array of length at least N+3 (N + '-', '.', '\0')
// - x must be have than N leading digits (before decimal) or "#\0" is returned
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
{
int j, k, r;
float y;
if (x<0.0) // handle negative numbers
{
*c++ = '-';
x = -x;
}
for (j=0; x>=1.0; j++) // j digits before decimal point
x /= 10.0; // .. and scale x to be < 1.0
if (j>N) // return error string if too many digits
{
*c++ = '#';
*c++ = '\0';
return;
}
y = pow(10, (float) N); // round to N digits
x = round(x * y) / y;
if (x>1.0) // if 1st digit rounded up ...
{
x /= 10.0; // then normalize back down 1 digit
j++;
}
for (k=0; k<N; k++)
{
r = (int) (x*10.0); // leading digit as int
x = x*10-r; // remove leading digit and shift 1 digit
*c++ = r + '0'; // add leading digit to string
if (k==j-1 && k!=N-1) // add decimal point after j digits
*c++ = '.'; // ... unless there are N digits before decimal
}
*c++ = '\0';
}
void DisplayResistance(float x)
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Adds the resistance value, x, to the display buffer without refreshing the display
// - converts to kohm, milliohm or microohm if necessary
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
{
static const unsigned char PROGMEM omega_bmp[] = // omega (ohm) symbol
{ B00000011, B11000000,
B00001100, B00110000,
B00110000, B00001100,
B01000000, B00000010,
B01000000, B00000010,
B10000000, B00000001,
B10000000, B00000001,
B10000000, B00000001,
B10000000, B00000001,
B10000000, B00000001,
B01000000, B00000010,
B01000000, B00000010,
B01000000, B00000010,
B00100000, B00000100,
B00010000, B00001000,
B11111000, B00011111 };
char s[8];
char prefix;
if (x>=1000.0) // display in killo ohms
{
x /= 1000.0;
prefix = 'k';
}
else if (x<0.001) // display in micro ohms
{
x *= 1000000.0;
prefix = 0xe5; // mu
}
else if (x<1.0) // display in milli ohms
{
x *= 1000.0;
prefix = 'm';
}
else
prefix = ' '; // display in ohms
f2str(x, 5, s);
// display computed resistance
display.setTextSize(2);
display.setTextColor(WHITE);
display.setCursor(0,20);
display.print(s);
// display prefix
display.setCursor(85,20);
display.print(prefix);
// display omega (ohms) symbol
display.drawBitmap(103, 18, omega_bmp, 16, 16, WHITE);
}
void DisplayDebug(int a, int b, float x, float y, float Vbat)
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Adds debug info to the display buffer without showing the updated display
// - Adds 2 ints (a, b) and a float(Vbat) to the top line and 2 floats (x, y)
// to the bottom line+, all in small (size 1) text
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
{
// display x, y in lower left, small font
display.setTextSize(1);
display.setCursor(0,45);
display.print(x,3);
display.print(" ");
display.print(y,3);
// display a, b in upper left, small font
display.setTextSize(1);
display.setCursor(0,0);
display.print(a);
display.print(" ");
display.print(b);
// display Vbat in upper middle, small font
display.setTextSize(1);
display.setCursor(60,0);
display.print(Vbat,1);
}
void DisplayStr(char *s)
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Adds a string, s, to the display buffer without refreshing the display @ (0,20)
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
{
display.setTextSize(2);
display.setTextColor(WHITE);
display.setCursor(8,20);
display.print(s);
}
#ifdef TESTMODE
void loop()
{
while (digitalRead(P_PushToTest))
;
DriveP();
display.clearDisplay();
DisplayStr("Drive: +");
display.display();
delay(250);
while (digitalRead(P_PushToTest))
;
DriveN();
display.clearDisplay();
DisplayStr("Drive: -");
display.display();
delay(250);
while (digitalRead(P_PushToTest))
;
DriveOff();
display.clearDisplay();
DisplayStr("Drive: Off");
display.display();
delay(250);
}
#endif
void setup()
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// - initializae display and I/O ports
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
{
DriveOff(); // disable current drive
Wire.begin(); // join I2C bus
display.begin(SSD1306_SWITCHCAPVCC, 0x3c, 0); // initialize display @ address 0x3c, no reset
pinMode(P_PushToTest, INPUT_PULLUP); // measure push button switch, active low
debug_mode = !digitalRead(P_PushToTest); // if pushed during power on, then debug mode
pinMode(P_Debug, OUTPUT); // debug port
}
void loop()
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// main measurement loop
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
{
const float Rr = 10.0; // reference resistor value, ohms
const float Rcal = 1.002419; // calibration factor
const int N = 2; // number of cycles to average
const int M = 50; // samples per half cycle
static long Toff;
double Rx; // calculated resistor under test, ohms
byte PGAr, PGAx; // PGA gains (r = reference, x = test resistors)
float Vr, Vx, Wx, Wr; // voltages in V
float Rn; // calculated resistor under test, ohms, single sample
double Avgr, Avgx; // average ADC readings in mV
int j, k, n;
float Vbat; // battery voltage in V (from 2:1 divider)
char serialbuff[10]; // Buffer for sending the reading over I²C
display.clearDisplay();
DisplayStr("measuring");
display.display();
// determine PGA gains
DriveP();
Wr = ADS1115read(ADS1115_CH01, ADS1115_6p144);
Wx = ADS1115read(ADS1115_CH23, ADS1115_6p144);
DriveN();
Vr = -ADS1115read(ADS1115_CH01, ADS1115_6p144);
Vx = -ADS1115read(ADS1115_CH23, ADS1115_6p144);
// measure battery voltage ... while drive is on so there is a load
Vbat = analogRead(A3)*5.0/1024.0; // 2:1 divider (5V FS) on 4.2v lithium battery
DriveOff();
PGAr = CalcPGA(max(Vr, Wr)); // determine optimum PGA gains
PGAx = CalcPGA(max(Vx, Wx));
// measure resistance using synchronous detection
Avgr = Avgx = 0.0; // clear averages
Rx = 0.0;
n = 0;
for (j=0; j<N; j++) // for each cycle
{
DriveP(); // turn on drive, positive
for (k=0; k<M; k++)
{
digitalWrite(P_Debug, 1);
Vx = ADS1115read(ADS1115_CH23, PGAx);
digitalWrite(P_Debug, 0);
Vr = ADS1115read(ADS1115_CH01, PGAr);
Avgx += Vx;
Avgr += Vr;
Rn = Vx/Vr;
if (Rn>0.0 && Rn<10000.0)
{
Rx += Rn;
n++;
}
}
DriveN(); // turn on drive, negative
for (k=0; k<M; k++)
{
digitalWrite(P_Debug, 1);
Vx = ADS1115read(ADS1115_CH23, PGAx);
digitalWrite(P_Debug, 0);
Vr = ADS1115read(ADS1115_CH01, PGAr);
Avgx -= Vx;
Avgr -= Vr;
Rn = Vx/Vr;
if (Rn>0.0 && Rn<10000.0)
{
Rx += Rn;
n++;
}
}
}
DriveOff();
Rx *= Rr * Rcal / n; // apply calibration factor and compute average
Avgr *= 1000.0 / (2.0*N*M); // average in mV
Avgx *= 1000.0 / (2.0*N*M);
// display the results ... battery icon, Rx measurement, debug info if requested
display.clearDisplay(); // ... and display result
BatteryIcon((Vbat-3.0)/(4.2-3.0)); // 7.5V = 0%, 9V = 100%
//display.drawLine(0, 8, 127, 8, WHITE); //Draw separator line under icons
if (n==0){ // no measurement taken ...
display.setTextSize(2);
display.setCursor(51,20);
display.print(F("OL"));
}
//DisplayStr("-----");
else
DisplayResistance(Rx);
//Send Reading via I²C
Wire.beginTransmission(0x50);
Wire.write(dtostrf(Rx, 5, 5, serialbuff));
Wire.endTransmission();
if (debug_mode)
DisplayDebug(PGAr, PGAx, Avgr, Avgx, Vbat);
display.display(); // show the display
// and then wait for next measurement request
Toff = millis()+60000L;
while(digitalRead(P_PushToTest)) // loop until measure button pressed
{
// Enter power down state for 120ms with ADC and BOD module disabled
//LowPower.powerDown(SLEEP_120MS, ADC_OFF, BOD_OFF);
if (millis()>Toff) // after 7 seconds ...
{
display.clearDisplay(); // clear display
display.display();
}
}
}

Hi, is is possible to measure Internal Battery Resistance with this tester?
Hi,
Unfortunately no. This unit does not have a battery impedance test.
#error(“Height incorrect, please fix Adafruit_SSD1306.h!”);
arduino 1.8.7 error message ??? in line 30….?????
thanks for answer!
have a nice days!!
Hi Aldo,
In Adafruit_SSD1306.h
1. uncomment #define SSD1306_128_64
2. comment #define SSD1306_128_32
3. comment #define SSD1306_96_16
In the example ssd1306_128x64_i2c
4. add #define SSD1306_LCDHEIGHT 64
on top of
#if (SSD1306_LCDHEIGHT != 64)
#error(“Height incorrect, please fix Adafruit_SSD1306.h!”);
#endif
Hope that helps! Cheers!
Hi,
Please show the modified circuit diagram.
Thanks.
OK ……….EVERY THING IS GOING ON VERY GOOD!!!
THANKS A LOT FOE HELP!!!!!
HAVE A NICE DAYS!!!!
Hi guys, Is it possible to use a 7 pin IPS ST7735S display in place of the 4pin? Was thinking D11, A6 and A7 could be used for the other 3?
Hi DBon,
There’s no reason why you couldn’t do that, but it would require a bit of code refactoring for the new display.
Cheers
Yeah i am familiar with the tft library but i am strugling to get anything to print to the screen at all. Ill have more of a play and see what i find. Thanks for the reply 🙂