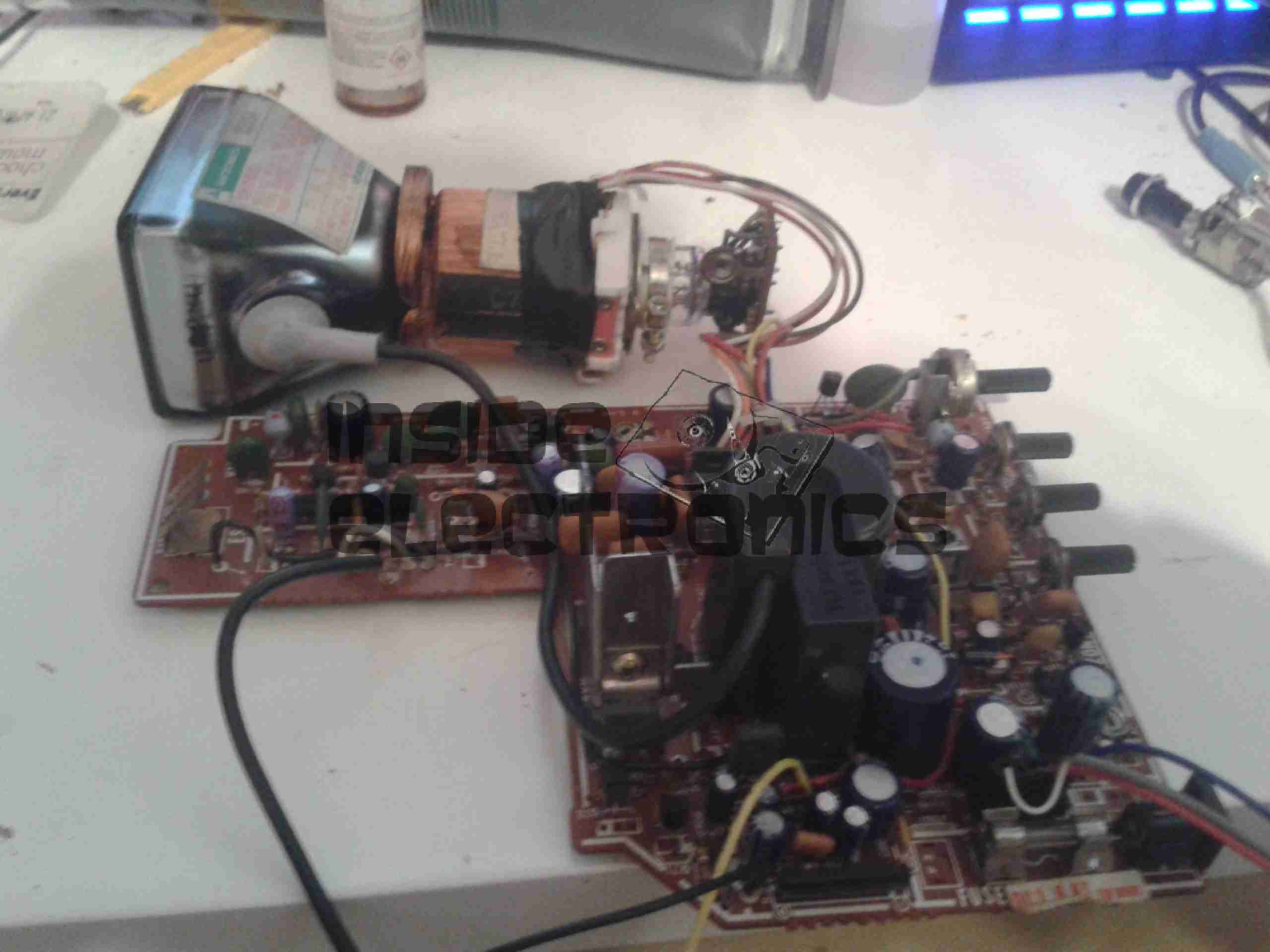
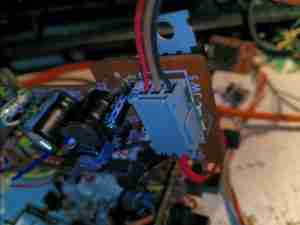
It’s time for another CRT-based post! This time it’s a Matsushita 40CB4-based viewfinder from 1980. These came from JVC colour tube cameras, and are physically massive! I’ve already worked out the pinout on the multicore cable here & attached a usable connector.

There’s lots of information on the bottom label of this unit, including a notification in German that the X-Ray emission from the device is shielded, and the maximum CRT acceleration voltage is 8kV. This last point is a bit strange, since the 40CB4 datasheet states a maximum design voltage on the final anode of 6kV. I did measure the voltage at the anode cup, and it’s stable at 7.15kV!

Popping a couple of screws out & removing the enormous eye cup allows the top cover to come off. This unit is very tightly packed inside, with 3 PCBs! The magnifying lens (~45mm diameter) & mirror on the left enlarge & turn the image so the camera operator can see it. The CRT’s at the top, with a copper grounding band around the face.

The CRT face is neatly slotted into the plastic housing, with the tally LEDs to the right of it. The legends on the LEDs are naturally printed in reverse, since they’re intended for viewing through the mirror. The optical section is entirely spray painted black for better contrast & stray light control.

The other 5″ of the casing is packed with electronics to support the CRT. The bottom PCB even “wraps around” to the right, with copper staples connecting the boards together. The CRT tube itself is hiding inside the deflection yoke and under a foam pad at the top of the unit. It’s secured in place with a copper grounding strap wrapped around the face of the tube, and a spring. A single screw secures the strap to the case. This also provides a local earth for the outer Aquadag coating on the tube, which is the negative plate of the final anode smoothing capacitor. The other plate is formed by the coating on the inside of the CRT glass, and the dielectric is of course the glass itself.
The main anode wire snakes off from the flyback at bottom left to the anode cup at the top of the CRT, insulating the 7kV from everything else.
There aren’t many reasons to jack up the final anode voltage on a CRT, past the design voltage of the tube as JVC have done here. The only plausible one I could think of is to increase brightness of the image, but the Sony 4CB4-based units I have only run at around 3kV, and those are plenty bright enough! The downside here of course, is that with higher energy electrons and a brighter image, the phosphor of the CRT will wear out faster.
Increasing voltage also increases X-Ray emission, but even at the 8kV maximum, such X-Rays would be so weak as to not make it through the CRT faceplate glass, which is loaded with lead anyway.
There’s not much sense in yanking the tube out of this unit, it’s identical to the Sony one’s I’ve done in the past:


Slotted into a gap above the CRT is a large TO-220 2SD476 NPN transistor, this is part of the power circuit; it’s the series pass element regulating the input 12v down to 9v for all the remaining circuits. The aluminium sheet on the back provides some heatsinking as this part gets warm! Current draw of this unit with no video input is about 260mA.

Popping the CRT out allows a view of the Vertical & Power Board. This hosts the input linear voltage regulator, and the vertical output control circuitry. Hiding at the back on the right is a NEC µPC1031H2 Vertical Deflection Controller.

Separating the boards reveals the other two PCBs, the Video & Horizontal/HV boards. The bottom board takes care of the Horizontal output, and the lefthand board the video input, sync separation & amplification.

The Horizontal section is controlled by a Matsushita AN294 device. Unfortunately I haven’t been able to locate a datasheet for this one. The flyback transformer (Horizontal Output) is on the right, with another smaller transformer I don’t quite know the purpose of. Oddly, there’s no large switching transistor for the horizontal output stage – as the PCB notes the flyback as being a “HVM” this may in fact be more tightly integrated with some of the drive circuitry in the potting. There aren’t anywhere near as many pins on it as a usual CRT flyback has either.
This section also generates the other voltages required by the CRT – 2.8v for the filament, and ~80v & ~400v for the grids.

A closeup of the video board shows the relative simplicity. Only 4 transistors are doing all the video actions. There is relatively high voltage on here though – an 85v feed from the power supply which is the rail voltage for the video amplifier to the CRT cathode/G1.

There’s a few adjustments available on this unit, here are the Focus & Horizontal Frequency (Hold) pots. Amazingly, even though this unit is about 43 years old at the time of writing, the unit fired straight up when I applied power & a composite video signal, with no adjustments required at all!
Unfortunately there’s no service manual or schematics that I could find on the web for this or the camera it came from, but connections to make this unit work are very simple:
| Wire Colour | Signal Name |
|---|---|
| YELLOW | +12V DC |
| BLACK | GND |
| Coax - Core | Composite Video 1v p-p |
| Coax - Shield | Composite Video GND |
There’s another blogger who’s done this particular viewfinder, but they didn’t dig into the unit anywhere near as far as I usually do:
https://hex.ro/wp/blog/matsushita-40cb4-mini-crt/
This blog has a lot of CRT-based viewfinder teardowns, mainly from newer cameras. It’s an interesting read.
Datasheets for the important parts (the ones I could find!) below: