Recently I decommissioned some networking equipment, and discovered the power supplies in some switches were single rail 12v types, with a rather high power rating. I figured these would be very good for powering my Ham radio gear.
They’re high quality Delta Electronics DPSN-150BP units, rated at a maximum power output of 156W.

These supplies have an adjustment pot for the output voltage regulation, but unfortunately it just didn’t have quite enough range to get from 12.0v to 13.8v. The highest they would go was ~13.04v.
After taking a look at the regulator circuit, I discovered I could further adjust the output voltage by changing a single resistor to a slightly lower value.
Firstly though, a little background on how switched mode power supplies operate & regulate their output voltage.

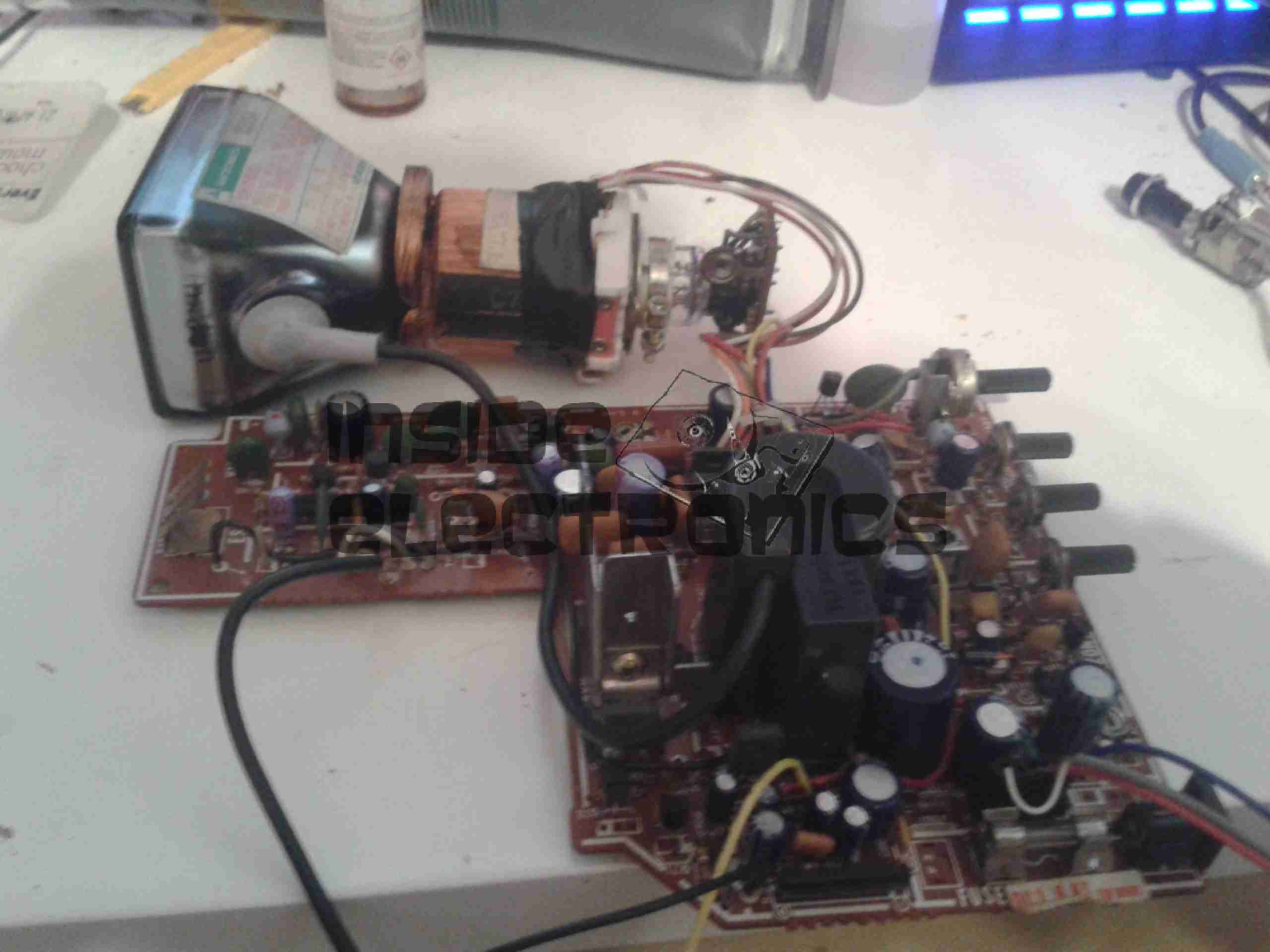
Here’s the supply. It’s mostly heatsink, to cool the large power switching transistors.
The first thing a SMPS does, is to rectify the incoming mains AC with a bridge rectifier. This is then smoothed by a large electrolytic capacitor, to provide a main DC rail of +340v DC (when on a 240v AC supply).

Above is the mains input section of the PSU, with a large common-mode choke on the left, bridge rectifier in the centre, and the large filter capacitor on the right. These can store a lot of energy when disconnected from the mains, and while they should have a discharge resistor fitted to safely drain the stored energy, they aren’t to be relied on for safety!
Once the supply has it’s main high voltage DC rail, this is switched into the main transformer by a pair of very large transistors – these are hidden from view on the large silver heatsinks at the bottom of the image. These transistors are themselves driven with a control IC, in the case of this supply, it’s a UC3844B. This IC is hidden under the large heatsink, but is just visible in the below photo. (IC5).


Here’s the main switching transformer, these can be much smaller than a conventional transformer due to the high frequencies used. This supply operates at 500kHz.
After the main transformer, the output is rectified by a pair of Schottky diodes, which are attached to the smaller heatsink visible below the transformer, before being fed through a large toroidal inductor & the output filter capacitors.
All this filtering on both the input & the output is required to stop these supplies from radiating their operating frequency as RF – a lot of cheap Chinese switching supplies forego this filtering & as a result are extremely noisy.
After all this filtering the DC appears at the output as usable power.
Getting back to regulation, these supplies read the voltage with a resistor divider & feed it back to the mains side control IC, through an opto-isolator. (Below).

The opto isolators are the black devices at the front with 4 pins.

For a more in-depth look at the inner workings of SMPS units, there’s a good article over on Hardware Secrets.
My modification is simple. Replacing R306 (just below the white potentiometer in the photo), with a slightly smaller resistor value, of 2.2KΩ down from 2.37KΩ, allows the voltage to be pulled lower on the regulator. This fools the unit into applying more drive to the main transformer, and the output voltage rises.
It’s important to note that making too drastic a change to these supplies is likely to result in the output filter capacitors turning into grenades due to overvoltage. The very small change in value only allows the voltage to rise to 13.95v max on the adjuster. This is well within the rating of 16v on the output caps.
Now the voltage has been sucessfully modified, a new case is on the way to shield fingers from the mains. With the addition of a couple of panel meters & output terminals, these supplies will make great additions to my shack.
More to come on the final build soon!