
Here’s a piece of medical equipment that in recent years has become extremely cheap, – a Pulse Oximeter, used to determine the oxygen saturation in the blood. These can be had on eBay for less than £15.

This one has a dual colour OLED display, a single button for powering on & adjusting a few settings. These cheap Oximeters do have a bit of a cheap plastic feel to them, but they do seem to work pretty well.
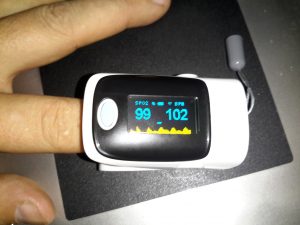
After a few seconds of being applied to a finger, the unit gives readings that apparently confirm that I’m alive at least. 😉 The device takes a few seconds to get a baseline reading & calibrate the sensor levels.

The plastic casing is held together with a few very small screws, but comes apart easily. here is the top of the main board with the OLED display panel. There appears to be a programming header & a serial port on the board as well. I’ll have to poke at these pads with a scope to see if any useful data is on the pins.

The bottom of the board has all the main components of the system. The microcontroller is a STM32F03C8T6, these are very common in Chinese gear these days. There’s a small piezo beeper & the main photodiode detector is in the centre.
There is an unpopulated IC space on the board with room for support components. I suspect this would be for a Bluetooth radio, as there’s a space at the bottom left of the PCB with no copper planes – this looks like an antenna mounting point. (The serial port on the pads is probably routed here, for remote monitoring).
At the top left are a pair of SGM3005 Dual SPDT analogue switches. These will be used to alternate the red & IR LEDs on the other side of the shell.
A 4-core FFC goes off to the other side of the shell, bringing power from the battery & supplying the sensing LEDs.

Power is supplied by a pair of AAA cells in the other shell.

The sensor LEDs are tucked in between the cells, this dual-diode package has a 660nm red LED & a 940nm IR LED.












































