
Well it’s time for a new DMM. After the last pair of eBay El-Cheapo Chinese meters just didn’t last very well, I decided a proper meter was required. This one is a Tenma 72-10405, stocked by Farnell for under £60. Not quite as many festures as the cheapo Chinese meters, but I expect this one to be a bit more reliable.

Since I can’t have anything without seeing how it’s put together, here’s the inside of the DMM. (Fuse access is only possible by taking the back cover off as well. The 9v PP3 battery has a seperate cover).

He’s the input section of the meter, with the 10A HRC fuse & current shunt for the high-amps range. The other fuse above is for the mA/µA ranges. The back cover has a wide lip around the edge, that slots into a recess in the front cover, presumably for blast protection if the meter should meet a sticky end. The HRC fuses are a definite improvement over the cheap DMMs, they only have 15mm glass fuses, and no blast protection built into the casing.
There are some MOVs for input protection on the volts/ohms jack, the jacks themselves are nothing more than stampings though.

Not much at the other side of the board, there’s the IR LED for the RS232 interface & the beeper.

Most of the other components are on the other side of the PCB under the LCD display. The range switch is in the centre, while the main chipset is on the left.

The chipset of this meter is a FS9922-DMM3 from Fortune Semiconductor, this is a dedicated DMM chipset with built in ADCs & microcontroller.


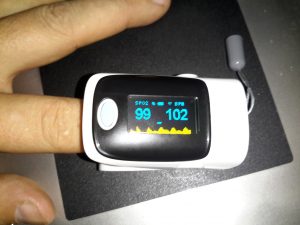
 The device takes a few seconds to get a baseline reading & calibrate the sensor levels.
The device takes a few seconds to get a baseline reading & calibrate the sensor levels.












