Recently my phone decided it was going to die a battery-related death, and having not found much useful information on the Great Google, (all the information I could find, was hinting at many issues from firmware to a faulty motherboard, nobody seems to have actually done any investigation into similar issues), I decided to dig into the phone to try & repair the problem.

The phone would work correctly for a while, then with the slightest movement or knock, would spontaneously switch off, and not turn back on without being whacked on a hard surface.
This symptom pointed me at a power connection problem. After removing the back of the phone (glass & heavily glued in place, so an awkward process), This was what I was presented with on the cell flex PCB.
In the above photo, the positive connection to the flex is fractured just after the solder joint with the BMS board.

I managed to scrape some of the insulation off the flex PCB & solder a jumper on to restore power. Unfortunately, this repair generated another fault, where the battery level was always shown at 50%, and plugging into a USB supply wouldn’t charge the phone. The other two pins on the cell are for communication & temperature sensing, clearly one of these traces was also broken in the flex.
The above photo has a pair of very small wire tails as well, for connecting an external charger.
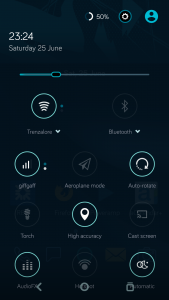
Here’s a screenshot of the phone with the original cell, even though it’s at about 4.15v (virtually fully charged). The battery management is having trouble talking to the phone, so for safety reasons, the charging logic refuses point-blank to charge the thing up.

The connector on the cell & phone motherboard is absolutely tiny, so I didn’t fancy attempting to solder on any bridge wires to try & bypass the broken flex.

The cell BMS has some intelligence on board, besides the usual over-current, over-charge & under-charge protection. The very small IC on the right has a Microchip logo, and the marking FT442, but I was unable to dig up any datasheets. The current sense resistor is directly connected to this IC, along with the main power FET to the left.

On the other side of the BMS board is another IC, again unidentifiable, and what looks like a bare-die, or CSP IC.
At this stage I figured the only way forward was to buy a new battery, eBay turned one up for less than £5. Above is the new battery fitted to the phone, datestamped 2014, so definitely old stock.
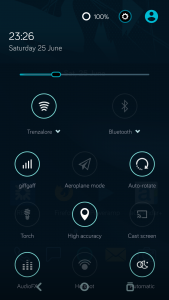
Booting the phone with the new battery quickly lets me know the fix worked, with a 100% reading & the ability to again charge properly!