Being in technology for a long time, I have seen my fair share of disk failures. However I have never seen a single instance where SMART has issued a sufficient warning to backup any data on a failing disk. The following is an example of this in action.

Here is a 2.5″ Toshiba MQ01ABD050 500GB disk drive. This unit was made in 2014, but has a very low hour count of ~8 months, with only ~5 months of the heads being loaded onto the platters, since it has been used to store offline files. This disk was working perfectly the last time it was plugged in a few weeks ago, but today within seconds of starting to transfer data, it began slowing down, then stopped entirely. A quick look at the SMART stats showed over 4000 reallocated sectors, so a full scan was initiated.
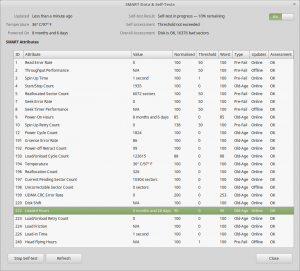
After the couple of hours an extended test takes, the firmware managed to find a total of 16,376 bad sectors, of which 10K+ were still pending reallocation. Just after the test finished, the disk began making the usual clicking sound of the head actuator losing lock on the servo tracks. Yet SMART was still insisting that the disk was OK! In total about 3 hours between first power up & the disk failing entirely. This is possibly the most sudden failure of a disk I’ve seen so far, but SMART didn’t even twig from the huge number of sector reallocations that something was amiss. I don’t believe the platters are at fault here, it’s most likely to be either a head fault or preamp failure, as I don’t think platters can catastrophically fail this quickly. I expected SMART to at least flag that the drive was in a bad state once it’s self-test completed, but nope.

After pulling the lid on this disk, to see if there’s any evidence of a head crashing into a platter, there’s nothing – at least on a macroscopic scale, the single platter is pristine. I’ve seen disks crash to the point where the coating has been scrubbed from the platters so thoroughly that they’ve been returned to the glass discs they started off as, with the enclosure packed full of fine black powder that used to be data layer, but there’s no indication of mechanical failure here. Electronic failure is looking very likely.
Clearly, relying on SMART to alert when a disk is about to take a dive is an unwise idea, replacing drives after a set period is much better insurance if they are used for critical applications. Of course, current backups is always a good idea, no matter the age of drive.









